TRIETHANOLAMINE (TEA) INTRODUCTION
Triethanolamine (TEA) is an organic chemical compound that belongs to the ethanolamine family. It is a versatile compound used in various industrial and consumer applications due to its unique chemical properties.
Basic Information
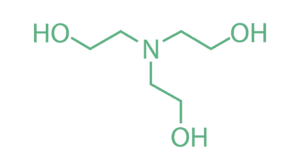
- Chemical Formula : N(CH₂CH₂OH)₃
- Molecular Weight : 149.19 g/mol
- IUPAC Name : 2,2′,2”-Nitrilotriethanol
Chemical Structure
- TEA consists of three ethanol groups (-CH₂CH₂OH) attached to a single nitrogen atom, forming a tertiary amine and a triol (compound with three hydroxyl groups).
Physical Properties
- Physical State : Colorless to pale yellow, viscous liquid
- Melting Point : 20.5 °C
- Boiling Point : 335.4 °C
- Density : 1.124 g/cm³ at 20 °C
- Solubility : Miscible with water, alcohol, and acetone
- Odor : Slight ammonia-like odor
Chemical Properties
- Basicity : TEA is a weak base and can react with acids to form salts.
- Hydrophilic Nature : Due to its multiple hydroxyl groups, TEA is highly soluble in water and other polar solvents.
- Stability : TEA is stable under normal conditions but can react with strong oxidizing agents.

Applications of TRIETHANOLAMINE (TEA)
- Surfactants and Detergents :
– Foaming Agents : TRIETHANOLAMINE (TEA) is used to produce anionic and non-ionic surfactants, which are key ingredients in shampoos, liquid soaps, and household cleaners. These surfactants enhance foaming and cleaning properties.
– Emulsifiers : TRIETHANOLAMINE (TEA) helps to stabilize emulsions, ensuring consistent texture and performance in various cleaning products. - Personal Care Products :
– Cosmetics : TEA is used in lotions, creams, and other cosmetics as a pH adjuster, emulsifier, and stabilizer. It helps to maintain the stability and consistency of these products.
– Shaving Creams : Used to improve the texture and foaming properties of shaving creams and gels.
– Hair Care : Found in shampoos and conditioners to enhance cleaning and conditioning properties. - Textile Processing :
– Lubricants and Anti-static Agents : TEA is used in textile processing to produce lubricants and anti-static agents, improving the handling and quality of textiles. - Gas Treatment :
– Acid Gas Removal : TRIETHANOLAMINE (TEA) can be used to remove acidic gases like carbon dioxide (CO₂) and hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) from natural gas and refinery gas streams, similar to MEA and DEA. - Pharmaceuticals :
– Formulations : TEA acts as an emulsifier and solubilizer in pharmaceutical formulations, helping to enhance the stability and effectiveness of medicinal products. - Metalworking Fluids :
– Corrosion Inhibition : TEA is used in metalworking fluids as a corrosion inhibitor and pH buffer, protecting metal surfaces from rust and corrosion. - Cement and Concrete :
– Grinding Aids : TEA is used as a grinding aid in the production of cement, improving the efficiency of the grinding process and the quality of the final product. - Coatings and Adhesives :
– Neutralizing Agent : TRIETHANOLAMINE (TEA) is used as a neutralizing agent and dispersant in coatings, adhesives, and sealants, ensuring uniform consistency and stability.
Packing of TRIETHANOLAMINE (TEA):
- Bulk in seagoing vessels/barges
- Bulk in flexitank cars
- Bulk in road tank cars
- Bulk in iso tank containers
Other packaging solutions are possible by agreement.
Safety and Handling Of (TEA)
- Health Hazards : TEA can cause skin and eye irritation. Prolonged exposure may lead to dermatitis and other skin conditions.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) : Use appropriate PPE such as gloves, safety goggles, and protective clothing when handling TEA.
- Storage : Store TEA in a cool, well-ventilated area away from strong acids, oxidizers, and other incompatible materials.
- First Aid Measures :
- Skin Contact : Wash affected area with plenty of water. Seek medical attention if irritation persists.
- Eye Contact : Rinse eyes thoroughly with water for at least 15 minutes. Seek immediate medical attention.
- Inhalation : Move the person to fresh air. If breathing difficulties occur, provide oxygen and seek medical attention.
- Ingestion : Do not induce vomiting. Rinse mouth with water and seek immediate medical attention.
Environmental Impact
- Aquatic Toxicity : TEA can be harmful to aquatic organisms and should be managed to prevent environmental contamination.
- Biodegradability : TEA is biodegradable, but measures should still be taken to minimize its release into the environment.
In summary, triethanolamine (TEA) is a widely used chemical in various industrial and consumer applications, thanks to its versatile properties as a surfactant, emulsifier, and pH adjuster. However, it requires careful handling and management to mitigate health and environmental risks.
TECHNICAL DATA SHEET OF TRIETHANOLAMINE (TEA) 85%
| Property | Specifications | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Clear and substantially free matter | ST-30.1 of suspended |
| Equivalent weight | 161 – 173.5 | ST-5.5 |
| Triethanolamine | wt% Measure | 70 min |
| Water, wt% | 13 – 17 | Loading Measure |