Introduction to Cutback Bitumen- A Key Player in Road Surfacing
Cutback bitumen, as the name suggests, is a bituminous binder that has been “cut back” or diluted with a solvent to decrease its viscosity and enhance its ability to coat aggregates. This substance is a vital player in the construction and maintenance of roads, particularly in situations where the traditional hot mix asphalt is not feasible due to temperature constraints or equipment limitations.
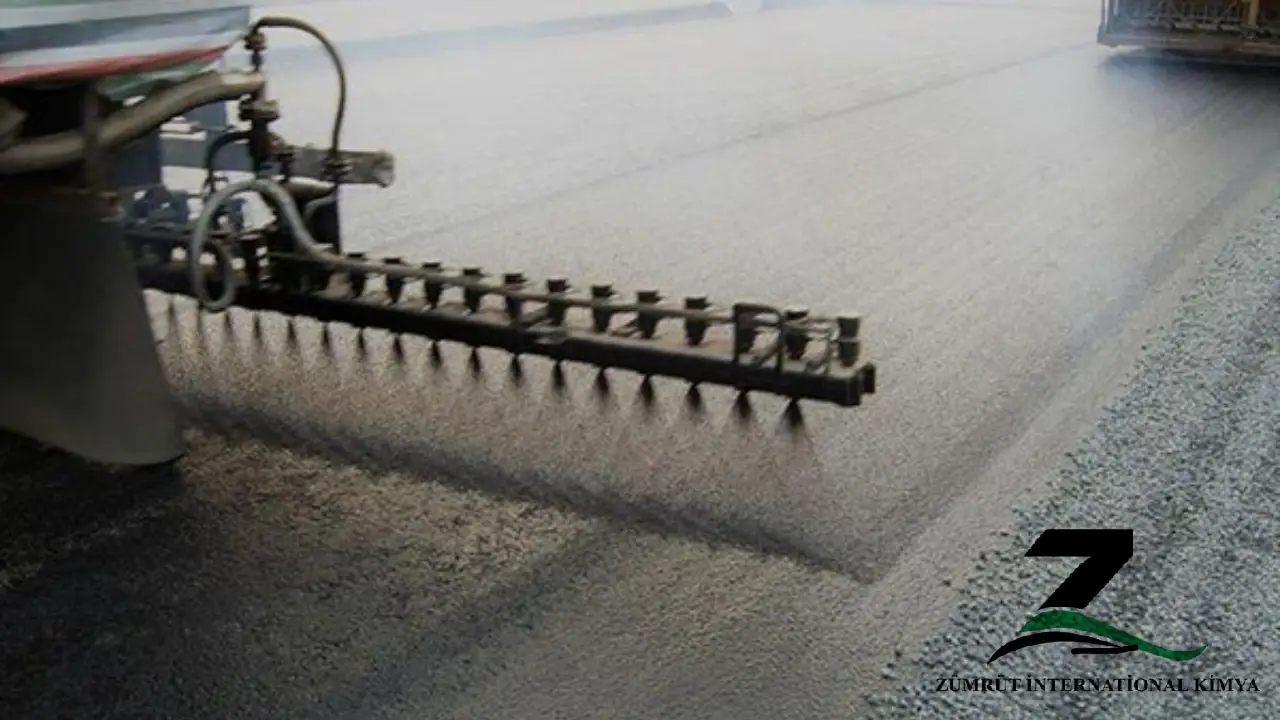
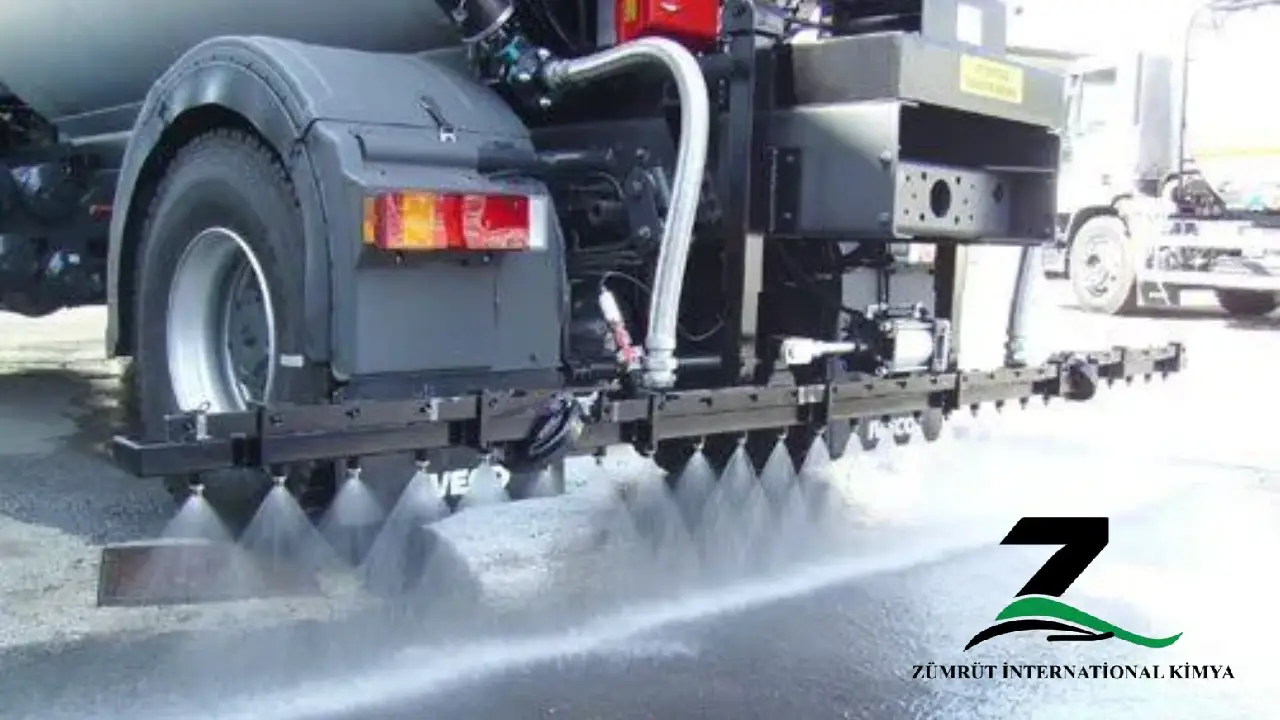
Bitumen in its natural state is solid and hard to work with. To improve its workability and to enable its usage at lower temperatures, solvents are added to the bitumen. This process turns it into cutback bitumen, which remains liquid even at room temperatures. The use of cutback bitumen is especially beneficial in road surfacing as it can be sprayed or mixed with aggregates in unheated conditions, making the road construction process faster and more cost-effective.
There are three primary types of cutback bitumen, classified based on the evaporation rate of the solvent: Rapid-Curing (RC), Medium-Curing (MC), and Slow-Curing (SC). These variations allow for the tailored use of cutback bitumen based on the specific needs of the road construction project, such as local climate, traffic loads, and available aggregates.
In road construction, cutback bitumen is used in surface dressings, prime coats, and tack coats. It’s also employed in patch repairs and maintenance, a testament to its versatility in the road surfacing sector. The solvent in the cutback bitumen gradually evaporates once applied, leaving behind the original bitumen to bind the aggregates, forming a sturdy and long-lasting road surface.
Despite its various benefits, the use of cutback bitumen has sparked environmental concerns due to the emission of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) from the evaporating solvents. This challenge has paved the way for the development of more environmentally friendly alternatives, like emulsified bitumen.
Nevertheless, cutback bitumen remains a key player in road surfacing worldwide, largely due to its ease of use, adaptability to different climatic conditions, and effectiveness in road surfacing applications.
Understanding the Production Process of Cutback Bitumen
The production of cutback bitumen involves the blending of a bituminous binder with a solvent or cutter. This process reduces the viscosity of the bitumen, making it more fluid, manageable, and suitable for cold weather applications. Here, we delve into the intricate steps involved in the manufacturing process of cutback bitumen.
- Selection of Bitumen: The first step is the selection of the appropriate grade of bitumen. This could be penetration grade bitumen, oxidized bitumen, or hard grade bitumen, depending on the desired properties of the final cutback bitumen product.
- Selection of Solvent or Cutter: The next step involves choosing the right solvent or cutter. The type of solvent determines the curing time of the cutback bitumen, classifying it into Rapid-Curing (RC), Medium-Curing (MC), or Slow-Curing (SC) types. Kerosene, diesel, naphtha, or other distillates are typically used as solvents.
- Blending Process: In this stage, the chosen bitumen and solvent are blended together. This is usually done in a special heated tank, under controlled conditions, to ensure complete mixing. The percentage of solvent added usually ranges from 10% to 50%, depending on the type of cutback bitumen being produced.
- Quality Control: Quality checks are performed throughout the production process to ensure the produced cutback bitumen meets the desired specifications. The penetration, viscosity, ductility, and flashpoint are among the properties that are routinely tested.
- Packaging and Storage: Once the quality checks are passed, the cutback bitumen is then transferred to storage tanks, ready for transport. It must be stored under appropriate conditions to prevent the solvent from evaporating and the bitumen from hardening.
It’s important to note that despite its many advantages, the production process of cutback bitumen does involve the use of volatile solvents which contribute to air pollution. This has led to an increased interest in the development and use of alternative, more environmentally friendly bituminous products such as emulsions and polymer modified bitumen.
In conclusion, the production of cutback bitumen is a carefully controlled process that requires the selection of the appropriate materials and strict adherence to manufacturing protocols to ensure the final product is of the highest quality.
The Significant Role of Cutback Bitumen in Road Construction
Cutback bitumen plays a crucial role in the construction, repair, and maintenance of roads, offering a range of benefits that make it an essential material in modern infrastructure development. Its unique properties, derived from the addition of solvents to standard bitumen, help address several challenges faced during road construction and surface treatments. Below is an exploration of the significant role that cutback bitumen plays in road construction:
- Improving Workability and Handling
One of the most significant advantages of cutback bitumen is its reduced viscosity, which makes it easier to handle and apply, especially in cooler weather or when working with large volumes of material. Regular bitumen, when heated, can be difficult to manage, requiring high temperatures for flowability. Cutback bitumen, due to its solvent content, remains at a workable consistency even at lower temperatures, facilitating smoother and more efficient application.
– Application in Low-Temperature Conditions: In colder climates or seasons, cutback bitumen can be applied without the need for additional heating equipment, making it more cost-effective and practical. - Adhesion and Bonding in Road Construction
Cutback bitumen is widely used in various road construction applications to ensure proper adhesion between layers of materials, particularly between the underlying base and the surface layer. The solvents in the cutback bitumen aid in achieving a strong bond, ensuring that the road structure remains intact for longer periods.
– Prime Coat Application: In the initial stages of road construction, cutback bitumen serves as a prime coat, which helps to prepare the base material for the subsequent layers of asphalt or other materials.
– Tack Coat Application: Cutback bitumen is also applied as a tack coat to improve the bond between old and new asphalt layers during resurfacing projects. This is particularly important for maintaining smoothness and preventing surface failures. - Surface Dressing and Sealing
Another key application of cutback bitumen in road construction is in surface dressing and sealing treatments. These processes are used to improve the road surface, enhance skid resistance, and protect the road from the ingress of water, which could lead to structural damage over time. The solvent in cutback bitumen helps it spread easily and form a uniform coat on the road surface.
– Surface Dressing: Cutback bitumen is often used in surface dressing, where it is applied over the road surface and then covered with aggregates. The bitumen binds the aggregates together, providing a durable, skid-resistant finish that can extend the lifespan of the road.
– Crack Sealing: For maintenance of existing roads, cutback bitumen is used to seal cracks and prevent water from entering the underlying layers, which could cause further damage. Its low viscosity allows it to penetrate deep into cracks, forming a solid seal. - Cost-Effectiveness and Energy Savings
Cutback bitumen offers several cost advantages compared to traditional hot-mix asphalt. The reduction in viscosity allows for easier application, which can reduce energy costs associated with heating bitumen during production. In many cases, the solvent in cutback bitumen can make the material suitable for use in areas where higher viscosity materials would not be feasible without excessive energy expenditure.
Energy Efficiency: Unlike hot-mix asphalt, which requires high temperatures for mixing and application, cutback bitumen can be applied without needing to heat the material to such high temperatures, saving both energy and costs.
Labor Efficiency: The ease of handling and faster application process can reduce the labor required during construction projects, further reducing costs. - Versatility in Road Maintenance and Repairs
Cutback bitumen is an excellent choice for road repairs and maintenance projects, particularly for patching and filling minor cracks or surface defects. Its ability to adhere to a variety of materials and its flexibility make it ideal for addressing a range of issues in existing road surfaces.
– Patching: For areas with localized damage, cutback bitumen is used for patching roads. It can easily be applied to the damaged area, and once the solvent evaporates, it forms a solid, durable surface that is integrated well with the surrounding road.
– Crack Sealing: It is used to fill and seal cracks, preventing water infiltration, which is a major cause of road deterioration. The low viscosity of cutback bitumen allows it to penetrate deep into cracks, ensuring a thorough seal. - Environmental Considerations and Evolution
While cutback bitumen has been widely used for many years, its environmental impact is a consideration due to the volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released during the evaporation of solvents. However, as road construction practices evolve, so does the focus on environmentally friendly alternatives.
– Eco-Friendly Alternatives: As awareness of environmental issues grows, the road construction industry has begun to shift towards alternatives like emulsified bitumen, which has a lower environmental impact. These materials offer similar workability benefits without the harmful effects associated with solvent evaporation. - Durability and Performance in Extreme Conditions
Cutback bitumen is known for its ability to provide long-lasting performance in extreme weather conditions. The material remains durable under both high and low temperatures, making it suitable for a variety of climates, from hot, arid regions to cold, freezing environments. Once the solvent evaporates and the bitumen solidifies, it forms a stable, weather-resistant surface.
– Cold Weather Application: Its ability to work in cold temperatures without the need for heating makes it a go-to material for road construction and repairs in colder regions.
– Heat Resistance: After the solvent has evaporated, cutback bitumen maintains its integrity under high temperatures, ensuring that roads can withstand intense heat without significant degradation.

Comparing Cutback Bitumen with Other Bituminous Materials in Road Surfacing
- Cutback Bitumen vs. Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA): While both materials are extensively used for road surfacing, their application differs. HMA requires high temperature for laying and compaction, limiting its use in colder weather or remote locations without asphalt plants. Conversely, cutback bitumen remains workable at room temperature, making it suitable for such conditions.
- Cutback Bitumen vs. Emulsified Bitumen: Both materials are designed to be workable at lower temperatures. The significant difference is that cutback bitumen uses a petroleum solvent, which evaporates after application, whereas emulsified bitumen uses water as a medium to disperse tiny bitumen droplets. Emulsified bitumen is considered more environmentally friendly due to the absence of volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- Cutback Bitumen vs. Polymer Modified Bitumen (PMB): PMB is regular bitumen modified with polymers to enhance its properties, including resistance to deformation, aging, and cracking. While PMB provides superior performance, it’s more expensive and requires special handling and mixing equipment, unlike cutback bitumen.
- Cutback Bitumen vs. Warm Mix Asphalt (WMA): WMA is produced and laid at lower temperatures than HMA, saving energy and reducing emissions. However, it still requires a higher temperature than cutback bitumen and specialized additives or processes to reduce the mixture’s viscosity.
- Cutback Bitumen vs. Bitumen Emulsion in Cold Mix: Both are used in producing cold mix asphalt, but they differ in curing time and environmental impact. Cutback bitumen cures as the solvent evaporates, which can take time and emit VOCs. In contrast, bitumen emulsion sets by breaking and coalescing when in contact with aggregates, reducing the curing time and environmental impact.
In conclusion, while cutback bitumen has proven to be versatile and highly useful for various road construction applications, it’s important to choose the appropriate bituminous material based on specific project requirements, environmental considerations, and cost constraints. Despite its potential environmental impact, cutback bitumen remains a widely-used material due to its cost-effectiveness, ease of use, and suitability for different climates and conditions.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Cutback Bitumen in Road Surfacing
Cutback bitumen is a prevalent choice for road surfacing due to its unique set of advantages. However, as with any material, it also comes with certain disadvantages. This section will explore the pros and cons of using cutback bitumen in road construction.
Advantages:
- Ease of Use: Cutback bitumen is easy to apply, thanks to its liquid state at ambient temperatures. This makes it an excellent choice for cold weather conditions or remote locations where heating bitumen may not be feasible.
- Versatility: Cutback bitumen’s range of viscosity grades allows for customization based on specific project requirements. It can be used in various applications, including prime coat, tack coat, or even pothole repairs.
- Penetration Ability: Due to its fluid nature, cutback bitumen can penetrate and seal small voids and cracks in the road surface, offering enhanced durability and longevity.
- Cost-effective: It is generally less expensive compared to other types of modified bitumen, which makes it an attractive option, particularly for budget-constrained projects.
Disadvantages:
- Environmental Impact: The most significant downside of cutback bitumen is its environmental impact. The use of petroleum solvents leads to the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), contributing to air pollution.
- Curing Time: Cutback bitumen requires time for the solvent to evaporate to gain strength. This curing process can sometimes lead to delays, especially in cold or humid conditions.
- Flammability: Certain types of cutback bitumen contain highly flammable solvents, posing potential safety hazards during transportation and storage.
- Regulations: Due to its environmental impact, the use of cutback bitumen is restricted in certain countries, which requires alternative solutions.
In conclusion, while cutback bitumen is a practical and cost-effective solution for various road construction needs, it’s necessary to consider its environmental and safety implications. The industry continues to innovate and develop more sustainable and efficient alternatives to address these challenges. However, until such alternatives can fully match the benefits of cutback bitumen, it remains an important part of the road construction toolkit.