- What is Cutback Bitumen? An In-Depth Look at Types and Applications
- Why Cutback Bitumen for Prime Coat and Tack Coat is Indispensable
- Understanding the Importance of Cutback Bitumen in Road Construction
- Prime Coat: Why Cutback Bitumen is the Go-To Material
- Tack Coat: Best Practices for Applying Cutback Bitumen
- Future Trends and Recommendations in the Use of Cutback Bitumen for Prime and Tack Coats
What is Cutback Bitumen? An In-Depth Look at Types and Applications
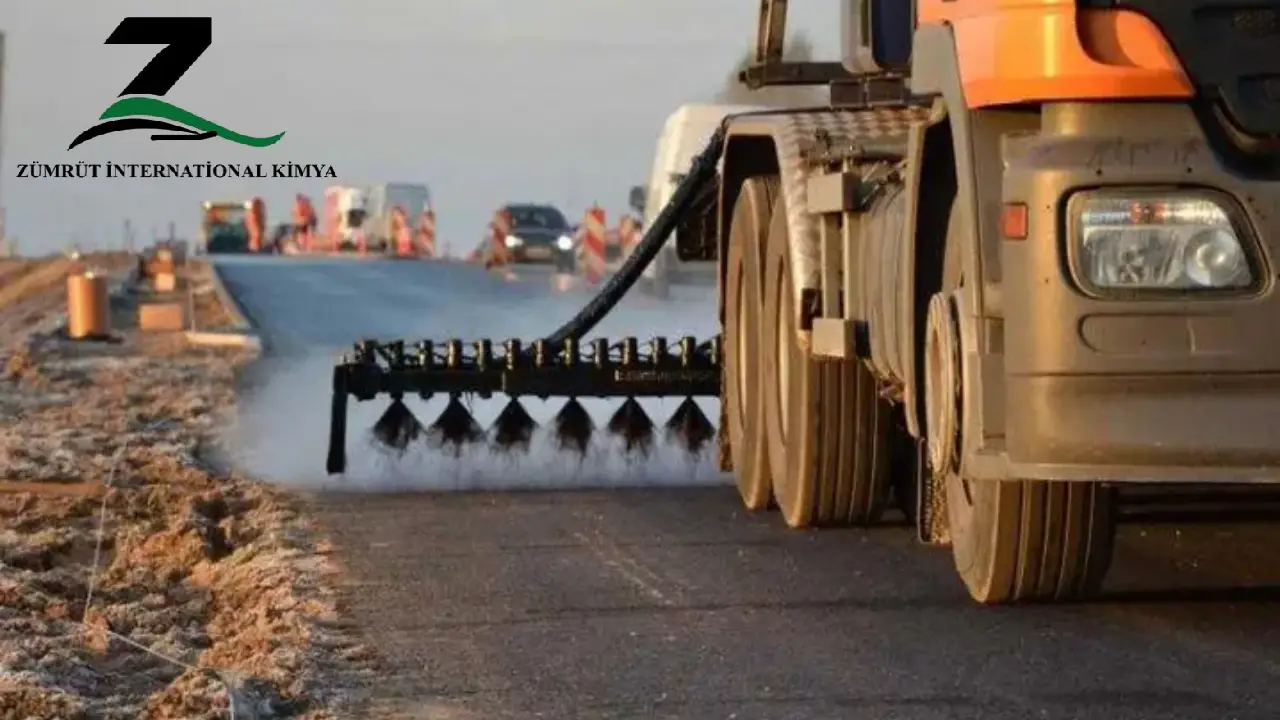
Cutback bitumen is a form of asphalt made by blending penetration-grade bitumen with a petroleum solvent to reduce its viscosity, making it easier to handle and apply. The solvent gradually evaporates after application, leaving behind the bitumen to bind materials together. It is widely used in road construction and maintenance due to its versatility and performance.
Types of Cutback Bitumen
Cutback bitumen is classified based on the rate at which the solvent evaporates:
- Rapid-Curing (RC)
Contains highly volatile solvents like naphtha or gasoline.
Quick evaporation rate.
Best suited for surface treatments, such as chip seals and tack coats. - Medium-Curing (MC)
Uses moderately volatile solvents like kerosene.
Evaporation is slower than RC types.
Ideal for prime coats and tack coats.
Common grades: MC-30, MC-70, MC-250, MC-800, and MC-3000. - Slow-Curing (SC)
Blended with low-volatile oils or heavy fractions.
Evaporation is slow, allowing longer working time.
Suitable for mixing with aggregates in road base and sub-base layers.
Applications of Cutback Bitumen
Cutback bitumen is used in various stages of road construction:
- Prime Coat
Purpose:
Stabilize and bind loose particles of granular base layers.
Create a waterproof barrier.
Prepare the surface for the application of asphalt layers.
Common Grade: MC-30. - Tack Coat
Purpose:
Provide a strong adhesive bond between existing surfaces and new asphalt layers.
Prevent delamination under traffic loads.
Common Grades: MC-70, MC-250. - Surface Treatments
Includes chip sealing and slurry sealing to enhance surface texture and skid resistance.
Rapid-curing grades (e.g., RC-70, RC-250) are commonly used. - Patching and Repairs
Used in repairing potholes and cracks due to its ease of application at ambient temperatures. - Dust Control
Applied to unpaved roads to minimize dust emissions and stabilize the surface.
Advantages of Cutback Bitumen
Ease of Application:
Can be applied at ambient temperatures, eliminating the need for extensive heating.
- Versatility:
Available in a variety of grades for different applications and climate conditions. - Strong Adhesion:
Provides excellent bonding between road layers and aggregates. - Penetration:
Medium-curing types penetrate deeply into granular surfaces, ensuring stability.
Why Cutback Bitumen for Prime Coat and Tack Coat is Indispensable
Cutback bitumen is indispensable for prime coat and tack coat applications in road construction due to its unique properties and performance benefits. Here’s why:
- Enhances Adhesion Between Layers
Prime Coat: Cutback bitumen penetrates deeply into granular or non-bound layers, binding loose particles and creating a stable foundation for subsequent layers. This ensures better cohesion and minimizes displacement under traffic loads.
Tack Coat: It creates a strong adhesive bond between the old and new asphalt layers, preventing delamination and ensuring long-term performance. - Superior Penetration and Waterproofing
For prime coats, the low viscosity of cutback bitumen (e.g., MC-30) allows it to penetrate deep into the base layer, improving structural integrity and providing a waterproof barrier. This prevents water ingress, which is a major cause of road damage. - Easy Application
Cutback bitumen is pre-mixed with a petroleum solvent, making it fluid at ambient temperatures. This eliminates the need for heating during application, simplifying the process and reducing operational costs. - Reliable Performance in Various Climates
Cutback bitumen grades (e.g., MC-30, MC-70, MC-250) are designed to cure effectively under a range of weather conditions. They are especially suitable for cooler climates where emulsified bitumen might struggle to set properly. - Proven Durability
Roads treated with cutback bitumen have a proven track record of durability and resilience. The material’s ability to provide a strong bond and waterproof protection enhances the lifespan of road surfaces. - Versatility
Cutback bitumen is available in various grades tailored for specific applications:
MC-30: Ideal for prime coats due to its excellent penetration.
MC-70 and MC-250: Commonly used for tack coats to ensure a robust bond between asphalt layers. - Cost-Effectiveness
The ease of storage, transportation, and application makes cutback bitumen a cost-effective solution for road construction projects, particularly in regions where high temperatures for asphalt heating are not feasible. - Compatibility with Various Aggregates
Cutback bitumen adheres well to a wide range of aggregates, ensuring uniform performance and reducing the risk of layer separation.
Understanding the Importance of Cutback Bitumen in Road Construction
Road construction is a complex discipline that relies on precision, durable materials, and the adoption of the latest technological advancements. One such essential material, crucial to achieving a long-lasting road infrastructure, is bitumen. Often referred to as asphalt or tar in colloquial terms, bitumen acts as a binder for aggregate particles, enabling the creation of asphalt concrete for road construction.
Among the various types of bitumen available, Cutback Bitumen has secured its position as a favorite for specific applications like Prime Coat and Tack Coat. But what makes Cutback Bitumen stand out?
In essence, Cutback Bitumen is produced by blending standard bitumen with solvents, typically kerosene or naphtha. This dilution process yields a fluid material that’s easier to work with, especially in cooler temperatures where standard bitumen may become too viscous. The solvents in the cutback evaporate over time, leaving behind the original bitumen properties, ensuring the robustness of the road structure.
The utilization of Cutback Bitumen for Prime Coat is especially prevalent. When we ask, “What is Prime Coat in road construction?”, we find that it acts as a preparatory layer, applied to an uncoated gravel or granular base before the asphalt overlay. This process ensures better adhesion, sealing off the base from moisture and providing a bond between the base and the overlay.
Furthermore, the application rate of the Prime Coat, its properties, and best practices play pivotal roles in the success of road projects. The same meticulous approach applies to the Tack Coat. While many might ponder over the difference between Prime Coat and Tack Coat, the latter serves as an intermediary layer between two asphalt layers, ensuring they bond correctly.
Given the environmental considerations today, it’s also essential to note the environmental impact of Cutback Bitumen. While it offers ease of application, there’s a responsibility on suppliers and those in road construction to ensure its use doesn’t negatively affect our ecosystem.
In subsequent sections, we will delve deeper into topics like Cutback Bitumen vs. Emulsified Bitumen, understanding their properties, and highlighting why suppliers prefer one over the other. Additionally, insights into best practices in applying Tack Coat and the specificities of Cutback Bitumen for Prime Coat will also be presented.
Stay with us as we navigate the intricate world of Cutback Bitumen and its undeniable significance in the realm of road construction
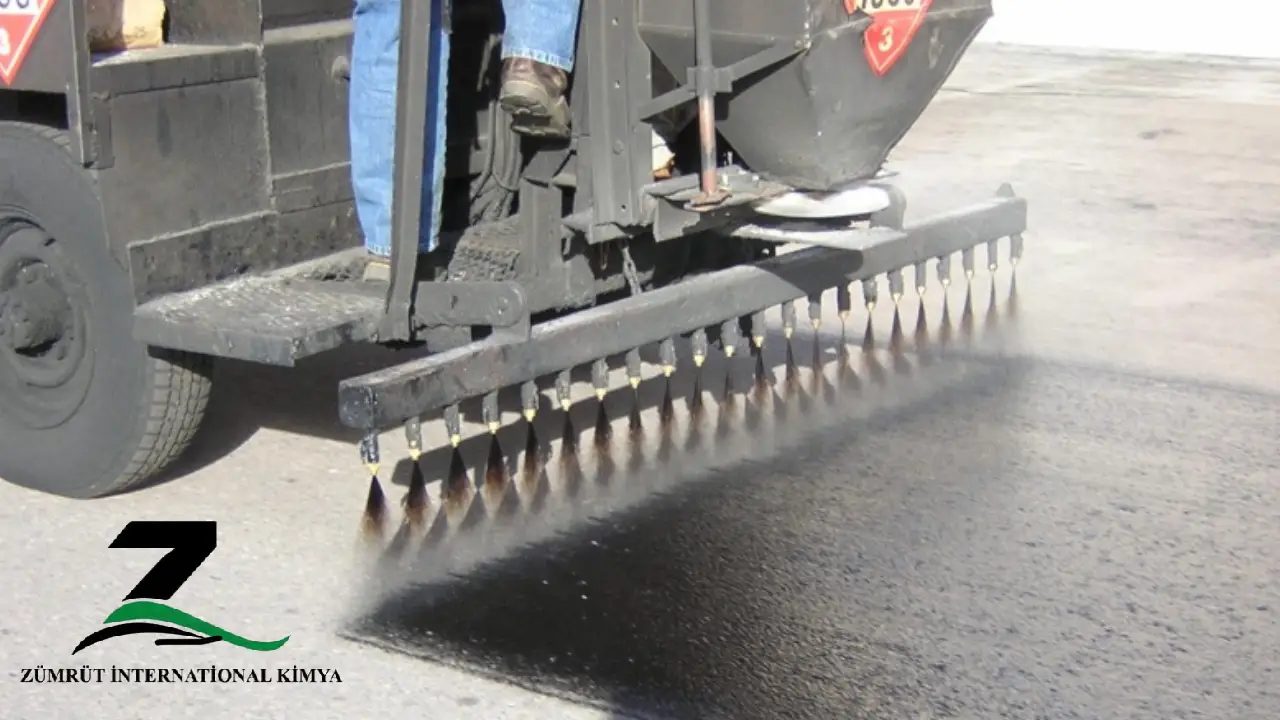

Prime Coat: Why Cutback Bitumen is the Go-To Material
Within the intricate fabric of road construction, one layer that plays a pivotal role, both as a preparatory measure and a sealing agent, is the Prime Coat. The success of subsequent asphalt layers largely hinges on the effectiveness of this underlying Prime Coat. Let’s delve into its specifics and understand why Cutback Bitumen emerges as the preferred choice.
Understanding the Prime Coat:
The term might evoke a plethora of questions, especially, “What is Prime Coat in road construction?” To elucidate, the Prime Coat serves as an intermediary layer, sandwiched between the uncompacted base (usually gravel or granular base) and the subsequent asphalt overlay. Its primary objectives are:
- Sealing: To prevent the infiltration of moisture into the base layer. Any seepage can jeopardize the integrity of the road structure, causing premature failures and reduced lifespan.
- Bonding: Ensuring a seamless and robust bond between the unbound base and the asphalt layer, enhancing the structure’s durability and resistance to traffic stresses.
The Role of Cutback Bitumen in Prime Coat:
Given the Prime Coat’s importance, the material choice becomes paramount. Enter Cutback Bitumen. The distinct characteristics of Cutback Bitumen make it ideal for the Prime Coat:
- Fluidity: Due to its diluted nature, Cutback Bitumen can easily penetrate the voids of the base layer, ensuring an even and thorough application. This fluidity is especially beneficial in cooler climates or regions where regular bitumen’s viscosity might pose challenges.
- Adhesion: Post evaporation of the solvents, Cutback Bitumen retains the adhesive qualities of standard bitumen, ensuring a strong bond between the base and the asphalt overlay.
- Flexibility: The “Prime Coat application rate” can be adjusted based on the type and specifications of the Cutback Bitumen used, allowing for adaptability to different road conditions and requirements.
- Ease of Application: The diluted nature not only aids in penetration but also ensures a smoother application process. Whether it’s spraying or manual spreading, Cutback Bitumen can be applied with relative ease.
Cutback Bitumen for Prime Coat vs. Alternatives:
While other materials like Emulsified Bitumen can be used for Prime Coating, Cutback Bitumen often has an edge:
- Rapid Setting: Unlike emulsions that require the water to evaporate, Cutback Bitumen, especially the Medium-Curing type, sets faster as the solvent evaporates, expediting the construction process.
- Consistency: While “Cutback Bitumen vs. Emulsified Bitumen” debates can hinge on environmental concerns, from a pure application perspective, the consistency and reliability of Cutback Bitumen often outweigh its counterparts.
In conclusion, the Prime Coat’s significance in road construction cannot be understated. And given its crucial role, the choice of Cutback Bitumen, with its adaptability, ease of application, and robust performance, stands validated. As road construction methodologies continue to evolve, the alliance between Prime Coat and Cutback Bitumen remains steadfast, testifying to their combined efficacy.
Tack Coat: Best Practices for Applying Cutback Bitumen
The effectiveness of road overlays hinges on the seamless bond between the existing pavement and the new asphalt layer. This bond is fortified by the Tack Coat – a thin, adhesive layer ensuring that the asphalt layers cohere robustly. Among the popular materials for the Tack Coat, Cutback Bitumen emerges prominently. However, its efficacy is amplified when applied with best practices. Let’s delve into the how-tos.
The Role of Tack Coat in Road Construction:
Before diving into best practices, it’s essential to understand the tack coat’s role. Think of it as the “glue” that holds the old and new asphalt layers together. This adhesive intermediary ensures:
- Uniform Load Distribution: A strong bond prevents slippage between layers, allowing vehicular loads to distribute evenly across the pavement structure.
- Longevity: Cohesive asphalt layers resist deformation, cracking, and other distresses, thereby extending the road’s lifespan.
“How to apply Tack Coat” – Best Practices:
- Surface Preparation: Ensure the surface is clean, devoid of dust, debris, or loose particles. Using blowers or brushes can be effective. Additionally, the surface should be reasonably dry; excessive moisture can hamper adhesion.
- Uniform Application: Achieving a consistent layer is critical. Utilizing distributor trucks with spray bars ensures that the Cutback Bitumen spreads uniformly. Overlaps and excessive material deposits should be avoided.
- Optimal Rate: It’s crucial to determine the “Tack Coat best practices” application rate. Too much can cause slippage, while too little can impede bonding. The rate can vary based on the texture and condition of the existing pavement.
- Curing Time: Allow the Cutback Bitumen tack coat to cure before overlaying the asphalt. This ensures that the solvent has evaporated, and the tack coat has achieved its desired viscosity.
- Temperature Considerations: Both the temperature of the Cutback Bitumen and the ambient temperature play roles in the application. Ensure the bitumen is at the recommended temperature range for optimal results.
- Equipment Calibration: Regularly calibrating the distributor trucks ensures the correct application rate and prevents wastage or under-application.
- Alternative Names and Materials: Be aware of the different terminologies or “names” people use for the product. Some might refer to it differently, but the essence remains the same. This knowledge can be crucial when sourcing materials or discussing projects with stakeholders.
Comparison with Alternatives:
- Cutback Bitumen vs. Emulsified Bitumen for Tack Coat: While both can be used for the tack coat, Cutback Bitumen often has a quicker break time, allowing for faster overlay. However, considerations like environmental impact and specific project requirements might influence the choice.
- Material Suppliers: Sourcing quality material is paramount. It’s beneficial to have a list of reputable “Cutback Bitumen for Prime Coat suppliers” to ensure the consistency and quality of the tack coat.
In the vast mosaic of road construction, the tack coat might appear as a minuscule layer. Yet, its role in ensuring the durability and performance of the pavement structure is undeniable. By adhering to best practices, particularly when applying Cutback Bitumen, road constructors can ensure that their pavements stand the test of time and traffic.
Future Trends and Recommendations in the Use of Cutback Bitumen for Prime and Tack Coats
The road construction industry is ever-evolving, adapting to new challenges and innovations. As we reflect upon the various aspects of Cutback Bitumen in the context of prime and tack coats, it’s essential to cast an eye towards the future and consider what trends may shape its usage, and what recommendations could be made for best practices.
Future Trends:
- Eco-Friendly Alternatives: As environmental consciousness grows, there will likely be a surge in the development and adoption of eco-friendly solvents for Cutback Bitumen, reducing VOC emissions and further aligning the material with green construction practices.
- Technological Advancements: With the rise of Industry 4.0, technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) may be integrated into the production and application of Cutback Bitumen, ensuring precision, efficiency, and reduced wastage.
- Material Enhancements: The push for roads that can withstand more extreme conditions may drive innovations in the formulation of Cutback Bitumen, making it even more resilient and durable.
- Sustainable Mining Practices: As raw materials for bitumen are extracted, future trends might see a more sustainable approach to mining, minimizing land degradation and environmental impact.
- Increased Recycling: The recycling of Cutback Bitumen and the roads constructed with it may become more prevalent, reducing the need for new raw materials and promoting a circular economy.
Recommendations:
- Research and Development: Stakeholders should invest in R&D to refine Cutback Bitumen formulations, addressing environmental concerns and enhancing material properties.
- Regular Training: To capitalize on the best practices for applying tack and prime coats, ongoing training for construction personnel is vital. This will ensure that the latest methods are utilized, optimizing the benefits of Cutback Bitumen.
- Collaboration with Environmental Agencies: Engaging with environmental bodies can provide insights into reducing the ecological footprint of Cutback Bitumen and adhering to regulations.
- Public Awareness: It’s essential to inform the public about the benefits of Cutback Bitumen roads, creating a favorable perception and facilitating community support for road projects.
- Diversifying Suppliers: For countries or companies relying heavily on imports, diversifying suppliers or considering local alternatives can ensure a consistent supply and potentially reduce costs.
- Safety First: Regardless of advancements, the safety of workers involved in the application of Cutback Bitumen should always be a top priority. Proper equipment, safety protocols, and regular checks can ensure a risk-free environment.