- Key Differences, Performance, Applications, and Sustainability” “Which is Best for Your Project?
- Introduction to Bitumen Emulsion and Cutback Bitumen
- Composition of Bitumen Emulsion vs. Cutback Bitumen
- Application Methods: Bitumen Emulsion vs. Cutback Bitumen
- Advantages of Bitumen Emulsion in Application:
- Application of Cutback Bitumen
- Comparison of Application Methods
- Environmental Impact
- Setting and Curing Times in Bitumen Emulsion and Cutback Bitumen
- Factors Influencing Setting and Curing in Cutback Bitumen:
- Setting and Curing Times in Comparison emulsion and cutback
Key Differences, Performance, Applications, and Sustainability” “Which is Best for Your Project?
As one of the most renowned manufacturers and pioneers in the production of cutback bitumen and bitumen emulsion in the Middle East, Zumrut Kimya stands as your reliable partner in the global development and maintenance of roads. Whether for new road construction, repair, or sustainability-focused projects, Zumrut Kimya ensures high-quality solutions for a wide range of climates and conditions, providing unmatched performance and expertise to projects around the world.
Introduction to Bitumen Emulsion and Cutback Bitumen
In road construction and maintenance, bitumen serves as a critical binding material, playing a pivotal role in ensuring the durability and strength of road surfaces. Among the various forms of bitumen available, bitumen emulsion and cutback bitumen are two widely used variants, each offering distinct properties and benefits depending on the project requirements.
- Bitumen Emulsion is a stable mixture of bitumen, water, and emulsifying agents. It allows bitumen to be applied at ambient temperatures without the need for heating. The emulsion contains tiny droplets of bitumen dispersed in water, making it suitable for use in cold or wet conditions.
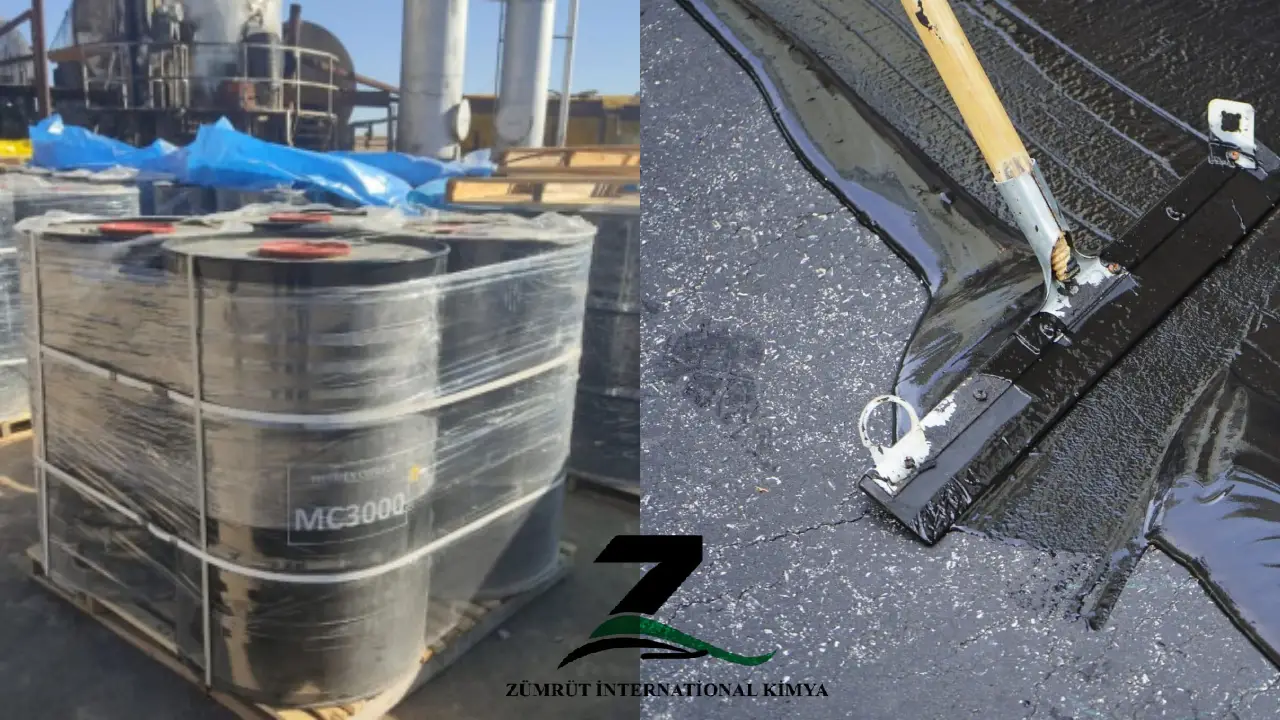
- Cutback Bitumen, on the other hand, is a form of bitumen that is diluted with solvents like kerosene or naphtha to reduce its viscosity. This enables easier application at lower temperatures. After application, the solvent evaporates, leaving the bitumen to bind the road materials.
Both materials are designed to address specific challenges in road construction, with key differences in their environmental impact, safety, and curing time. This chapter will explore the fundamental characteristics of bitumen emulsion and cutback bitumen, comparing their advantages, disadvantages, and common use cases.
Composition of Bitumen Emulsion vs. Cutback Bitumen
The fundamental difference between bitumen emulsion and cutback bitumen lies in their composition, which affects their application, behavior, and environmental impact.
- Bitumen Emulsion Composition
Bitumen emulsion is a two-phase system consisting primarily of:
- Bitumen (40-70% by weight): The main binding agent, responsible for adhesion and durability in road construction.
- Water (30-60% by weight): Acts as a carrier to disperse the bitumen, allowing the emulsion to be applied at ambient temperature without the need for heating.
- Emulsifying Agents: These are surfactants that help to stabilize the bitumen droplets in water. The emulsifier creates a charged layer around the bitumen droplets, preventing them from coalescing and maintaining a stable suspension. Emulsifiers can be:
- Anionic (negatively charged)
- Cationic (positively charged)
- Non-ionic
The choice of emulsifier affects the setting time of the emulsion and its interaction with different aggregates.
- Cutback Bitumen Composition
Cutback bitumen is a mixture of:
- Bitumen: The same binder used in emulsions, but with no water or emulsifying agents involved.
- Solvent (30-50% by weight): A petroleum-based solvent (e.g., kerosene, gasoline, or naphtha) is used to reduce the viscosity of bitumen, allowing it to be applied at lower temperatures. Once the solvent evaporates after application, the bitumen reverts to its original consistency, binding the aggregate.
- Rapid-Curing (RC) cutbacks use highly volatile solvents like gasoline.
- Medium-Curing (MC) cutbacks use moderately volatile solvents such as kerosene.
- Slow-Curing (SC) cutbacks use less volatile solvents like diesel.
Key Differences in Composition Comparison emulsion and cutback
- Water vs. Solvent: Bitumen emulsion uses water as a dispersant, while cutback bitumen uses petroleum-based solvents to lower viscosity.
- Emulsifier vs. None: Emulsion relies on an emulsifying agent to stabilize the mixture, while cutback bitumen doesn’t require this since it’s a simple solution of bitumen and solvent.
- Environmental Impact: The water in bitumen emulsion evaporates without harmful emissions, while the evaporation of solvents in cutback bitumen releases volatile organic compounds (VOCs), contributing to pollution.
In summary, while both emulsions and cutbacks serve the same basic purpose of making bitumen easier to apply, the inclusion of water and emulsifiers in emulsions makes them more environmentally friendly, whereas the use of solvents in cutbacks offers ease of application but at a higher environmental cost.
Application Methods: Bitumen Emulsion vs. Cutback Bitumen
The methods of applying bitumen emulsion and cutback bitumen differ significantly due to their composition, behavior in different environments, and curing processes. These differences affect how they are used in road construction and maintenance.
Application of Bitumen Emulsion
Bitumen emulsion is widely used in situations where low temperatures, wet conditions, or environmental concerns are critical. It can be applied cold and is particularly suited to projects aiming for sustainable and eco-friendly practices. The application methods include:
- Surface Dressing:
– A thin layer of bitumen emulsion is sprayed onto the road surface, followed by the application of aggregate chips. This process seals the road and improves skid resistance.
– The emulsion breaks upon contact with the aggregate, bonding it to the surface as the water evaporates. - Tack Coat:
– Bitumen emulsion is sprayed onto an existing asphalt surface to create a bonding layer before applying a new layer of asphalt. This ensures a strong adhesion between layers.
– The emulsion used for tack coats typically breaks quickly to allow for the continuation of construction work without delay. - Slurry Seals and Micro-Surfacing:
– A mixture of bitumen emulsion, fine aggregates, and water is spread over the surface to fill small cracks and restore the texture of worn pavements. This method is ideal for thin layers and rapid repairs. - Cold Mix Asphalt:
– Bitumen emulsion is mixed with aggregate at ambient temperature to create cold-mix asphalt. This mixture is often used for patching potholes, rural roads, or areas with limited access to hot-mix plants. - Prime Coat:
– A slow-setting bitumen emulsion is sprayed onto a granular base to penetrate and bind the underlying layer before asphalt is applied. This helps to stabilize the base and improve water resistance.
Advantages of Bitumen Emulsion in Application:
- Cold Application: Emulsions can be applied at ambient temperature, eliminating the need for heating, which saves energy and reduces risks.
- Versatility: They can be used in a wide range of weather conditions, including damp and cold environments.
- Environmentally Friendly: Since no harmful solvents are released, bitumen emulsion is a cleaner option, often preferred in areas with strict environmental regulations.
Application of Cutback Bitumen
Cutback bitumen is used when quick penetration or rapid setting is required. Since it contains solvents, it is applied at lower temperatures than hot bitumen, but some heating is still required in certain conditions. The application methods include:
1- Prime Coat:
- Cutback bitumen, typically in slow-curing form, is applied to granular bases before laying asphalt. The cutback penetrates the base material to stabilize and improve adhesion for the final road surface.
- The slow evaporation of the solvent ensures good penetration into the base layer.
2- Tack Coat:
- Cutback bitumen, usually in rapid-curing form, is applied between two layers of asphalt to create a bond.
It is typically applied when quick evaporation of the solvent is required to allow rapid continuation of road construction.
3- Spray Sealing:
- In this method, a layer of cutback bitumen is sprayed onto the road, followed by aggregates, which are embedded into the surface using rollers. This method is similar to surface dressing but is often used where quicker setting and curing are needed.
4- Patching and Maintenance:
- Cutback bitumen is used in quick repairs and patching works, especially in colder climates where hot mix asphalt is not viable. Medium-curing or rapid-curing cutbacks allow for easy handling and fast repairs.
Advantages of Cutback Bitumen in Application:
- Lower Viscosity: The use of solvents reduces the viscosity, making it easier to apply without requiring high temperatures.
- Quick Setting: Rapid-curing cutbacks allow for quick application and fast opening to traffic, making them ideal for projects that require minimal delays.
Comparison of Application Methods
| Aspect | Bitumen Emulsion | Cutback Bitumen |
| Composition | Water-based mixture with bitumen and an emulsifying agent. | Bitumen dissolved in petroleum-based solvents (e.g., kerosene, naphtha). |
| Application | Cold application, no heating required. | May require heating to lower viscosity. |
| Curing Process | Water evaporates or separates for bitumen to set. | Solvents evaporate to allow bitumen to set. |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, no VOC emissions. | Releases VOCs, contributing to air pollution. |
| Safety | Safer to handle; no fire risk or hazardous fumes. | Fire hazards and harmful fumes during application. |
| Cost | Lower long-term cost due to no heating; special storage needed in cold conditions. | Higher initial cost due to solvents and heating requirements. |
| Adhesion | Excellent adhesion to damp surfaces. | Strong adhesion after proper curing. |
| Durability | Durable under normal conditions. | Can weaken due to solvent evaporation over time. |
| Storage | Requires specialized storage to prevent freezing. | Easier to store in various conditions. |
| Use Cases | Tack coats, prime coats, and surface dressing in environmentally sensitive areas. | Suitable for cold climates and remote areas without advanced equipment. |
Environmental Impact
Sustainable Choice Between Bitumen Emulsion and Cutback Bitumen
The environmental impact of construction materials has become a significant concern in modern infrastructure projects, especially with the growing focus on sustainability. Bitumen emulsion and cutback bitumen, both widely used in road construction and maintenance, differ considerably in their environmental effects. This chapter explores how each material affects the environment and why bitumen emulsion is generally considered the more sustainable option.
Bitumen Emulsion: Eco-Friendly Composition
Bitumen emulsion is often preferred in environmentally conscious projects due to its eco-friendly nature. The key environmental benefits of bitumen emulsion include:
1- Water-Based Composition:
- Bitumen emulsion uses water as a dispersing medium, which means no harmful solvents or chemicals are involved. After application, the water evaporates naturally, leaving behind the bitumen to bind the road materials.
- Since water is the primary medium, bitumen emulsion does not release any hazardous volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere.
2- Lower Energy Consumption:
- Bitumen emulsion can be applied at ambient temperature, eliminating the need for high-temperature heating. This drastically reduces the amount of energy required during application, leading to a lower carbon footprint.
- The cold application also reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional hot-mix bitumen or cutback bitumen, which often require heating.
3- Minimal Health Hazards:
- Due to its lack of harmful solvents, bitumen emulsion poses minimal health risks to workers and nearby communities during application. There is no danger of inhaling toxic fumes or VOCs, making it safer for both workers and the environment.
4- Versatility in Cold and Wet Conditions:
- Since bitumen emulsion can be used in cold and wet conditions, it is particularly advantageous in regions where conventional hot bitumen or cutback bitumen may not be viable. This adaptability reduces the need for additional treatments or materials, further promoting sustainability.
Cutback Bitumen: Environmental Concerns
While cutback bitumen offers practical advantages, it comes with significant environmental drawbacks due to its reliance on solvents. The environmental impact of cutback bitumen includes:
1- Release of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs):
- Cutback bitumen contains petroleum-based solvents like kerosene, gasoline, or naphtha, which are used to reduce the viscosity of bitumen for easier application. These solvents evaporate into the atmosphere during and after application, releasing VOCs.
- VOC emissions contribute to air pollution, smog formation, and adverse health effects, particularly for workers exposed to the fumes and for residents near construction sites.
2- Higher Energy Consumption:
- Although cutback bitumen requires lower temperatures than hot-mix asphalt, some heating is still needed for certain applications. This requires more energy than cold-applied emulsions, contributing to a larger carbon footprint.
- The energy used for solvent production and transport also adds to the environmental cost.
3- Flammability and Safety Risks:
- The solvents used in cutback bitumen are flammable and pose safety risks during transport, storage, and application. Extra precautions are required to prevent fires, explosions, and hazardous spills, which further increases its environmental and safety burden.
4- Potential Soil and Water Contamination:
- If cutback bitumen is not applied or handled properly, it can lead to the contamination of surrounding soil and water due to solvent runoff. Solvent residues can leach into nearby water bodies, posing long-term environmental risks to ecosystems and drinking water supplies.
Sustainability Considerations
In modern road construction, sustainability goals often prioritize materials that minimize environmental degradation. Here’s how bitumen emulsion stands out in comparison to cutback bitumen:
- Carbon Footprint:
Bitumen emulsion has a lower carbon footprint since it does not require the use of heating or petroleum-based solvents. This makes it a more sustainable option in terms of energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. - Air Quality:
The absence of VOC emissions in bitumen emulsion makes it the cleaner choice for air quality. By contrast, the use of cutback bitumen contributes to air pollution through the release of VOCs during application. - Regulatory Compliance:
Many countries are imposing stricter environmental regulations that limit the use of materials releasing VOCs. This makes cutback bitumen less attractive as stricter regulations increase its long-term costs and usage limitations. Bitumen emulsion, on the other hand, aligns with modern environmental regulations and goals. - Lifecycle Impact:
Bitumen emulsion, due to its cold application and lack of solvents, has a lower overall environmental impact throughout its lifecycle, from production to application. Cutback bitumen, with its solvent production, transport, application, and VOC release, is associated with higher environmental costs over time.
The Sustainable Choice: Bitumen Emulsion
In conclusion, bitumen emulsion is the more sustainable and environmentally friendly option compared to cutback bitumen. Its water-based formulation, cold application process, and lack of harmful emissions make it a clear winner for eco-conscious road construction projects. With the increasing focus on reducing carbon emissions and adhering to strict environmental regulations, bitumen emulsion is poised to play a leading role in the future of sustainable infrastructure development.
On the other hand, cutback bitumen, while still widely used, presents significant environmental challenges due to its reliance on solvents and the release of VOCs. As sustainability becomes more central to construction practices, alternatives like bitumen emulsion are becoming more favored for their lower environmental impact and long-term benefits.
Setting and Curing Times in Bitumen Emulsion and Cutback Bitumen
The setting and curing times of bitumen emulsion and cutback bitumen are important factors that influence their use in road construction projects. These times determine how quickly traffic can be allowed on a freshly treated surface, how fast the material bonds with the aggregate, and the overall project timeline.

Bitumen Emulsion: Setting and Curing
In bitumen emulsion, the setting time refers to how quickly the water evaporates, allowing the bitumen to break (separate from the water) and bond with the aggregate or road surface. The curing time is when the emulsion fully sets, and the bitumen achieves its final strength and hardness.
Bitumen emulsions are classified into three categories based on how quickly they set:
1- Rapid Setting (RS):
- Setting Time: The emulsion breaks very quickly when it comes into contact with aggregate or is applied to a surface. This is ideal for surface dressing, where the emulsion needs to break and bond with the aggregate immediately after spraying.
- Curing Time: Full curing is achieved within a short period, making it possible to open the road to traffic relatively quickly.
Use Case: Surface dressing, where fast setting is required for rapid construction and minimal traffic disruption.
2- Medium Setting (MS):
- Setting Time: The emulsion breaks more slowly, which allows it to mix well with aggregate without premature setting. This is useful in cases where a longer working time is needed, such as in patching and sealing.
- Curing Time: Once set, the curing process can take a few hours, but the road can typically be opened to traffic shortly after application.
- Use Case: Cold mix asphalt, where slower setting is beneficial for thorough mixing with aggregate.
3- Slow Setting (SS):
- Setting Time: The emulsion takes a longer time to break, making it suitable for applications where extended working time is necessary, such as in slurry seals and cold-mix applications.
- Curing Time: Full curing may take several hours or even days, depending on environmental conditions like temperature and humidity. The longer setting time ensures even distribution of the emulsion in the mixture.
- Use Case: Slurry seals, micro-surfacing, and prime coats, where prolonged workability is required for even application.
Factors Influencing Setting and Curing in Bitumen Emulsion:
- Temperature and Humidity: Warmer temperatures and dry conditions accelerate the breaking and curing process.
- Aggregate Type: Some aggregates, particularly dry and absorbent types, speed up the breaking process by absorbing water from the emulsion.
- Emulsion Type: The choice of emulsifying agents determines whether the emulsion sets rapidly or slowly.
Cutback Bitumen: Setting and Curing
Cutback bitumen relies on the evaporation of solvents to set and cure. Unlike bitumen emulsion, where water evaporates to break the emulsion, the setting and curing times in cutback bitumen are dictated by how quickly the solvent evaporates.
Cutback bitumen is classified based on how fast the solvent evaporates,
which determines the setting and curing time:
– Setting Time: The solvent used (usually gasoline) is highly volatile and evaporates quickly. This leads to a rapid setting time, often within minutes to a few hours.
– Curing Time: The surface can cure fully within hours, allowing traffic to resume quickly. The bitumen reaches its final strength after the solvent has fully evaporated.
– Use Case: Rapid patching and tack coats, where quick setting and curing are necessary to minimize traffic disruption.
– Setting Time: The solvent (typically kerosene) evaporates at a moderate rate, resulting in a medium setting time. The process may take several hours, depending on ambient temperature and wind conditions.
– Curing Time: Complete curing can take up to a day or more, during which the cutback continues to harden as the solvent evaporates.
– Use Case: Prime coats and cold-mix applications, where more time is needed for the cutback to set and bind with aggregates.
– Setting Time: Slow-curing cutbacks use solvents with low volatility, such as diesel. These take longer to evaporate, leading to a slow setting time. This gives ample time for the bitumen to penetrate deep into the base layer.
– Curing Time: The curing process can take several days or even weeks, depending on environmental conditions. During this time, the solvent slowly evaporates, leaving behind the bitumen binder.
– Use Case: Prime coats on gravel roads or in areas where deep penetration into the base layer is required.
Factors Influencing Setting and Curing in Cutback Bitumen:
Solvent Type: The volatility of the solvent determines how quickly the cutback sets and cures.
Temperature: Higher temperatures accelerate solvent evaporation, speeding up the setting and curing process.
Wind and Air Circulation: Greater air movement promotes faster evaporation of the solvent, reducing the curing time.
Setting and Curing Times in Comparison emulsion and cutback
The setting and curing times of bitumen emulsion and cutback bitumen are important factors that influence their use in road construction projects. These times determine how quickly traffic can be allowed on a freshly treated surface, how fast the material bonds with the aggregate, and the overall project timeline.
Bitumen Emulsion: Setting and Curing
In bitumen emulsion, the setting time refers to how quickly the water evaporates, allowing the bitumen to break (separate from the water) and bond with the aggregate or road surface. The curing time is when the emulsion fully sets, and the bitumen achieves its final strength and hardness.
Bitumen emulsions are classified into three categories based on how quickly they set:
- Rapid Setting (RS):
- Medium Setting (MS):
- Slow Setting (SS):
Factors Influencing Setting and Curing in Bitumen Emulsion:
- Temperature and Humidity: Warmer temperatures and dry conditions accelerate the breaking and curing process.
- Aggregate Type: Some aggregates, particularly dry and absorbent types, speed up the breaking process by absorbing water from the emulsion.
- Emulsion Type: The choice of emulsifying agents determines whether the emulsion sets rapidly or slowly.
Cutback Bitumen: Setting and Curing
Cutback bitumen relies on the evaporation of solvents to set and cure. Unlike bitumen emulsion, where water evaporates to break the emulsion, the setting and curing times in cutback bitumen are dictated by how quickly the solvent evaporates.
Cutback bitumen is classified based on how fast the solvent evaporates, which determines the setting and curing time:
- Rapid Curing (RC):
- Medium Curing (MC):
- Slow Curing (SC):
Factors Influencing Setting and Curing in Cutback Bitumen:
- Solvent Type: The volatility of the solvent determines how quickly the cutback sets and cures.
- Temperature: Higher temperatures accelerate solvent evaporation, speeding up the setting and curing process.
- Wind and Air Circulation: Greater air movement promotes faster evaporation of the solvent, reducing the curing time.