- Description (PVC) in the automotive industry
- Key Applications of PVC in the Automotive Industry
- Advantages of PVC in Automotive Applications
- Why is PVC used in cars instead of other materials?
- How PVC helps reduce vehicle weight and fuel consumption
- Is PVC recyclable and how does it help save the environment in cars?
- Is (PVC) in automotive industry harmful to the environment?
Description (PVC) in the automotive industry
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) plays an essential role in the automotive industry due to its versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. It is widely used in various vehicle components, both interior and exterior, transforming how manufacturers design and construct cars. Here’s an overview of PVC’s key applications and benefits in the automotive sector:
Key Applications of PVC in the Automotive Industry
- Interior Components:
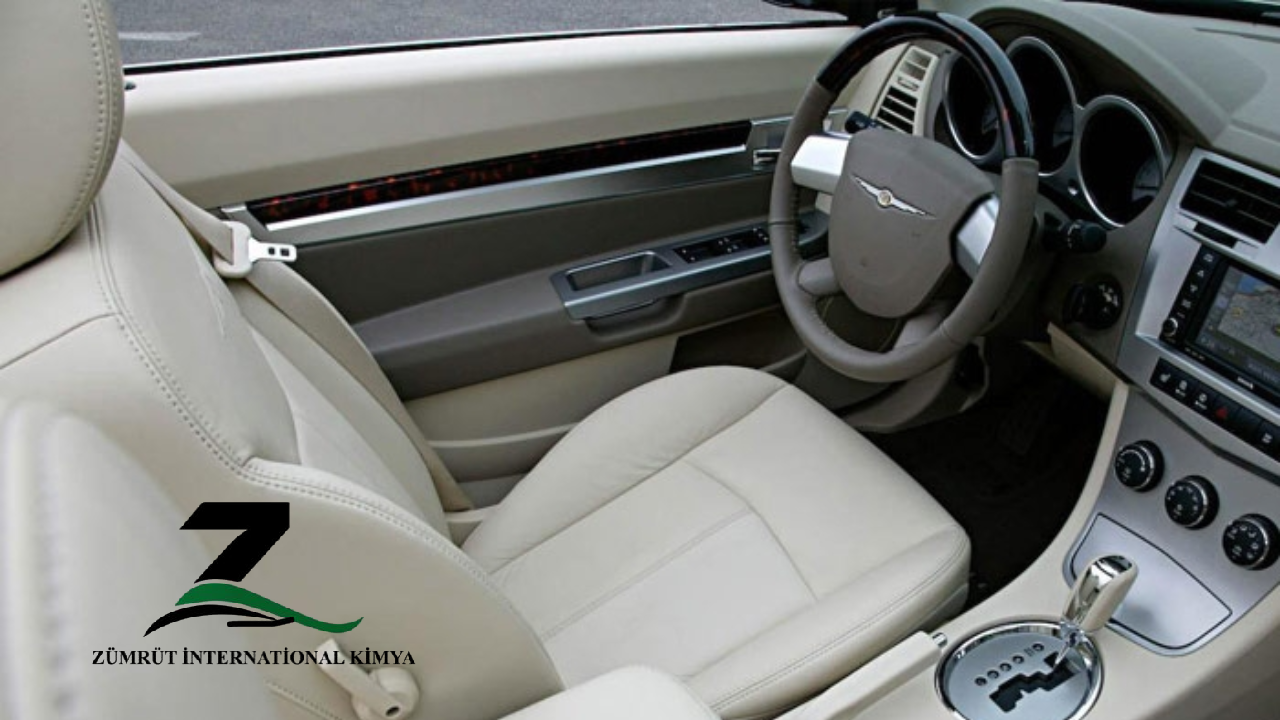
Seats and Upholstery: PVC is often used in car seats and upholstery, offering a leather-like finish that is both durable and easy to clean. It is resistant to stains and wear, maintaining quality over time.
Dashboard and Panels: For dashboards, door panels, and interior trims, PVC provides a smooth finish that withstands exposure to sunlight and high temperatures, maintaining its color and texture.
Floor Mats: PVC’s water resistance and durability make it an excellent material for floor mats, where it protects against dirt, moisture, and chemicals. - Exterior and Functional Components:
Underbody Coatings: Used as a protective layer, PVC helps shield a vehicle’s undercarriage from rust and corrosion, improving durability in various weather conditions.
Wire Insulation: PVC is ideal for insulating wires in the car’s electrical system due to its flexibility, heat resistance, and electrical insulation properties, which enhance vehicle safety. - Lightweight and Fuel Efficiency:
PVC’s lightweight nature, compared to traditional metals, contributes to overall vehicle weight reduction. Lighter vehicles consume less fuel, leading to better fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. - Environmental and Economic Benefits:
Cost-Effective Production: PVC is a cost-effective material for manufacturers, reducing production expenses while maintaining quality.
Recyclability: PVC can be recycled, aligning with the automotive industry’s sustainability goals by reducing waste and resource consumption. - Enhanced Safety:
Fire Resistance: PVC is inherently fire-resistant, which makes it safer for applications in vehicle interiors and wiring systems, reducing the risk of fire-related incidents.
Shock Absorption: PVC’s flexibility allows it to absorb impact, making it suitable for protective applications in the car structure.
Advantages of PVC in Automotive Applications
- Durability: PVC is highly resistant to wear and damage, extending the lifespan of components.
- Affordability: It offers a cost-effective alternative to more expensive materials, without sacrificing quality or safety.
- Sustainability: As a recyclable material, PVC contributes to eco-friendly practices in the industry.
PVC’s durability, adaptability, and cost-efficiency make it a cornerstone material in the automotive industry. Its contributions to lightweight design, enhanced safety, and sustainability underscore its critical role in meeting both modern automotive standards and environmental demands.
Why is PVC used in cars instead of other materials?
Due to its high resistance to wear, water, heat and lower cost, PVC is a suitable choice for the production of car parts. Also, its light weight helps to reduce fuel consumption and improve efficiency.
How PVC helps reduce vehicle weight and fuel consumption
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) plays a significant role in reducing vehicle weight, which directly impacts fuel consumption. Here’s how PVC contributes to this crucial aspect in automotive design:
- Lightweight Material Properties
PVC is inherently lightweight compared to traditional automotive materials like metals. Replacing metal components with PVC reduces the overall weight of the vehicle, making it more fuel-efficient. Lightweight vehicles require less energy to move, which translates to lower fuel consumption and reduced emissions. - Versatile Applications in Place of Heavier Materials
PVC is used in various automotive components such as interior trims, seat upholstery, door panels, and dashboard covers, which traditionally may have been made from heavier plastics or metal. By substituting these parts with PVC, manufacturers can reduce weight without compromising quality, durability, or aesthetics. - Lower Energy for Manufacturing
PVC requires less energy for manufacturing compared to some heavier materials, which indirectly reduces the vehicle’s embodied energy—the total energy used from material extraction to vehicle assembly. This approach supports an overall reduction in resource consumption, contributing to fuel economy over the vehicle’s lifecycle. - Improved Aerodynamics and Efficiency
The flexibility of PVC allows it to be molded into aerodynamic shapes for parts like exterior trims, which help reduce drag on the vehicle. Reduced drag leads to better fuel efficiency as the car requires less energy to overcome air resistance, especially at higher speeds. - Contribution to Electrification Efforts
In electric vehicles (EVs), where battery weight is already a concern, PVC’s lightweight properties make it a valuable choice for non-structural parts. By reducing the weight of non-essential components, PVC helps EVs achieve longer range, which is a key aspect of EV efficiency. - Compliance with Fuel Efficiency Standards
As automotive manufacturers face increasingly stringent fuel efficiency and emissions standards, the use of PVC supports compliance efforts by enabling the production of lighter, more fuel-efficient vehicles. This is especially crucial in meeting the requirements set by environmental regulations worldwide.

Is PVC recyclable and how does it help save the environment in cars?
- Recycling PVC Reduces Resource Consumption
- Lower Carbon Footprint Through Recycling
- Durability Reduces Waste and Promotes Longevity
- Closed-Loop Recycling Systems
- Less Plastic Waste in the Environment
- Supporting Eco-Friendly Practices in Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- Compliance with Environmental Regulations
Is (PVC) in automotive industry harmful to the environment?
The use of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) in the automotive industry has both environmental advantages and challenges. While PVC offers benefits such as recyclability and durability, which can support sustainable practices, certain aspects of PVC manufacturing and disposal can have environmental impacts. Here’s a balanced look at the pros and cons of PVC in terms of environmental impact in the automotive industry:
Environmental Benefits of PVC in Automotive Applications
- Durability and Longevity
PVC is highly durable and resistant to wear and weathering, which means automotive parts made from PVC last longer. This reduces the need for frequent replacements, lowering overall material consumption and waste generation. - Recyclability
PVC is recyclable, allowing car manufacturers to repurpose it into new products, including automotive components. This helps reduce reliance on new resources and decreases the amount of waste ending up in landfills. - Lightweight Material
PVC is lighter than many alternatives, which can reduce the weight of a vehicle, leading to improved fuel efficiency and lower emissions over the vehicle’s lifespan.
Environmental Challenges of PVC in Automotive Applications
- Production Process and Emissions
The production of PVC involves the use of chlorine and other chemicals that can release harmful pollutants, including dioxins, which are environmental contaminants. Proper regulation and management of emissions during production can help mitigate this impact. - End-of-Life Disposal Concerns
If not recycled, PVC can persist in the environment for a long time because it’s non-biodegradable. Improper disposal, such as incineration, can lead to the release of toxic fumes, including hydrogen chloride and dioxins, which are harmful to air quality and health. - Plasticizers and Additives
Some flexible forms of PVC use plasticizers, which can potentially leach out over time, especially if exposed to high temperatures. In automotive settings, regulatory standards typically control and minimize these risks, ensuring that additives are safe and low-leaching.
Mitigating the Environmental Impact of PVC
- Recycling Programs: Effective PVC recycling programs can reduce landfill waste and lower the need for new raw materials, thus minimizing environmental harm.
- Use of Eco-Friendly Additives: Manufacturers can opt for safer additives in PVC formulations, reducing the potential for harmful emissions.
- Regulated Manufacturing Processes: The PVC industry has been increasingly regulated, and advancements in production technology have reduced emissions, making the process more environmentally friendly over time.