DIETHANOLAMINE (DEA) INTRODUCTION
Diethanolamine (DEA) is an organic chemical compound with the formula HN(CH₂CH₂OH)₂. It is a secondary amine and a diol, combining the properties of both amines and alcohols. DEA is a colorless, viscous liquid with a slight ammonia-like odor. It is commonly used in various industrial and chemical applications.
Basic Information
- Chemical Formula : C₄H₁₁NO₂
- Molecular Weight : 105.14 g/mol
- Structure : DEA consists of two hydroxyethyl groups (-CH₂CH₂OH) attached to a nitrogen atom.
- IUPAC Name : 2,2′-Iminodiethanol
Physical Properties
- Physical State : Colorless to pale yellow, viscous liquid
- Melting Point : 28 °C
- Boiling Point : 268 °C
- Density : 1.097 g/cm³ at 20 °C
- Solubility : Miscible with water, alcohol, and acetone
- Odor : Slight ammonia-like
Chemical Properties
- Basicity : Diethanolamine (DEA) is a weak base and can react with acids to form salts.
- Esterification : Reacts with carboxylic acids to form esters.
- Amidation : Can form amides when reacted with acids.
- Reactivity : DEA can participate in various chemical reactions due to its amine and hydroxyl groups, making it a versatile intermediate.
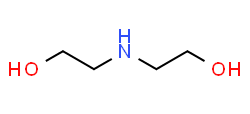
DIETHANOLAMINE (DEA)
Applications of Diethanolamine (DEA)
Diethanolamine (DEA) is a versatile compound used in various industrial and commercial applications due to its unique chemical properties. Here are some of the key applications of Diethanolamine (DEA):
- Surfactants and Detergents :
– Foaming Agents : DEA is used to produce surfactants such as Diethanolamine (DEA) lauryl sulfate, which are common in shampoos, liquid soaps, and bubble baths. These surfactants enhance foaming and cleaning properties.
– Emulsifiers : DEA helps stabilize emulsions in various cleaning products, ensuring consistent texture and performance. - Personal Care Products :
– Shampoos and Conditioners : Diethanolamine (DEA) is used in formulations to adjust pH, improve viscosity, and enhance the foaming and cleansing properties.
– Lotions and Creams : It acts as an emulsifier, helping to mix water and oil phases, providing a stable and homogenous product. - Gas Treatment :
– Acid Gas Removal : Diethanolamine (DEA) is employed in the treatment of natural gas and refinery gas streams to remove acidic gases like carbon dioxide (CO₂) and hydrogen sulfide (H₂S). This process is crucial for purifying gas and making it suitable for commercial use. - Textile Processing :
– Softening Agents : Diethanolamine (DEA) is used in the production of fabric softeners, which help in giving textiles a soft and smooth feel.
– Dye Dispersants : It acts as a dispersing agent for dyes and pigments, ensuring even distribution and better color quality. - Pharmaceuticals :
– Drug Synthesis : DEA serves as an intermediate in the synthesis of various pharmaceuticals, providing a building block for more complex chemical structures.
– Solubilizers and Emulsifiers : It is used to enhance the solubility and stability of medicinal formulations. - Agriculture :
– Herbicides and Pesticides : DEA is used in the formulation of herbicides and pesticides, improving their effectiveness and stability.
– Fertilizers : It can also be found in some agricultural chemicals to enhance nutrient absorption. - Corrosion Inhibition :
– Metalworking Fluids : Diethanolamine (DEA) is used as a corrosion inhibitor in metalworking fluids to protect metal surfaces from rust and corrosion.
– Boiler Water Treatment : It helps in preventing corrosion in boilers and other water-containing systems. - Concrete Additives :
– Grinding Aids : DEA is used in the production of cement as a grinding aid, improving the efficiency of the grinding process and the quality of the final product. - Lubricants :
– Additives : DEA is used as an additive in lubricants to improve their performance and protect engine parts from wear and corrosion. - Polyurethane Foams :
– Catalyst : DEA is used as a catalyst in the production of flexible and rigid polyurethane foams, which are used in furniture, insulation, and automotive applications.
DISTINGUISHING (TEA) (MEA) AND (DEA)
- MEA is primarily used for gas treatment, surfactant production, and as an intermediate in chemical synthesis.
- DEA is versatile in surfactant production, gas treatment, personal care products, pharmaceuticals, and corrosion inhibition.
- TEA is widely used in surfactants, personal care products, textile processing, pharmaceuticals, metalworking fluids, and as a cement grinding aid.
Each ethanolamine has unique properties that make it suitable for specific applications, reflecting its chemical structure and functional groups.
Toxicity and Safety of (DEA)
Diethanolamine (DEA) has notable health and environmental concerns, necessitating careful handling and usage. Here’s an overview of its toxicity and safety aspects:
Health Hazards
- Skin Irritation :
– DEA is corrosive and can cause significant irritation and burns upon contact with the skin. Prolonged or repeated exposure may lead to dermatitis. - Eye Irritation :
– DEA can cause severe eye irritation and damage, potentially leading to permanent eye injury if not properly treated. - Respiratory Irritation :
– Inhalation of DEA vapors or aerosols can irritate the respiratory tract, leading to coughing, sore throat, and shortness of breath. - Ingestion :
– Swallowing DEA can cause gastrointestinal distress, including nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. - Chronic Exposure :
– Prolonged or repeated exposure to DEA has been associated with liver and kidney damage.
– DEA is classified as a potential carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), particularly concerning its role in nitrosamine formation, which are known carcinogens.
Packing of Diethanolamine (DEA):
- Bulk in seagoing vessels/barges
- Bulk in flexitank cars
- Bulk in road tank cars
- Bulk in iso tank containers
Other packaging solutions are possible by agreement.
Environmental Impact
- Aquatic Toxicity :
– Diethanolamine (DEA) is harmful to aquatic organisms and can cause long-term adverse effects in aquatic environments. Care should be taken to prevent DEA from entering waterways. - Biodegradability :
– While Diethanolamine (DEA) is biodegradable, its presence in significant quantities can still pose risks to the environment. Proper disposal and treatment of waste containing DEA are necessary to minimize its impact.

Safety Measures
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) :
– Gloves : Use chemical-resistant gloves to prevent skin contact.
– Eye Protection : Wear safety goggles or a face shield to protect eyes.
– Respiratory Protection : Use appropriate respiratory protection if there is a risk of inhaling vapors or aerosols.
– Clothing : Wear protective clothing, such as long sleeves and lab coats, to minimize skin exposure. - Handling and Storage :
– Ventilation : Ensure adequate ventilation in areas where DEA is used to prevent the buildup of vapors.
– Storage : Store Diethanolamine (DEA) in a cool, well-ventilated area away from incompatible materials like strong acids, oxidizers, and materials that can react with amines.
– Spill Response : In case of a spill, evacuate the area, and use appropriate absorbent materials to contain and clean up the spill. Follow local regulations for disposal of contaminated materials. - First Aid Measures :
– Skin Contact : Immediately wash the affected area with plenty of water and remove contaminated clothing. Seek medical attention if irritation persists.
– Eye Contact : Rinse eyes thoroughly with water for at least 15 minutes, lifting eyelids to ensure complete flushing. Seek immediate medical attention.
– Inhalation : Move the person to fresh air. If breathing difficulties occur, provide oxygen and seek medical attention.
– Ingestion : Do not induce vomiting. Rinse mouth with water and seek immediate medical attention. - Emergency Procedures :
– Familiarize yourself with the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) or Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for DEA.
– Ensure that emergency eyewash stations and safety showers are readily accessible in areas where DEA is handled.
TECHNICAL DATA SHEET OF Diethanolamine (DEA)
| Appearance (MOA 200) | Clear liquid or white solid |
|---|---|
| Assay (MOA 549) | ≥ 99.0 wt% |
| Monoethanolamine (MOA 549) | ≤ 0.5 |
| Color (MOA 201) | ≤ 20 Hazen |
| Water (MOA 305) | ≤ 0.2 wt% |
| Triethanolamine (MOA 549) | ≤ 0.30 |
| Characteristics | |
| Form | Viscous liquid |
| Color | Colorless |
| Odor | Ammonical |
| Water solubilit | Completely |
| Solubility in other solvents | Acetone;Ethanol |
| pH, 10% solution | 11.5 |
| Melting point/freezing point, 1013 hPa | 27 °C |
| Boiling point/boiling range, 1013 hPa | 270 °C |
| Flash point, 1013 hPa | 100-199 °C |
| Ignition temperature | > 150 °C |
| Vapor pressure, 20°C | 0.00009 hPa |
| Density, 20°C | 1100 kg/m³ |
| Relative density, 20°C | 1.1 |
| Partition coefficient, N-octanol/water, 20°C, log Pow | -2.46 |