caustic soda peals
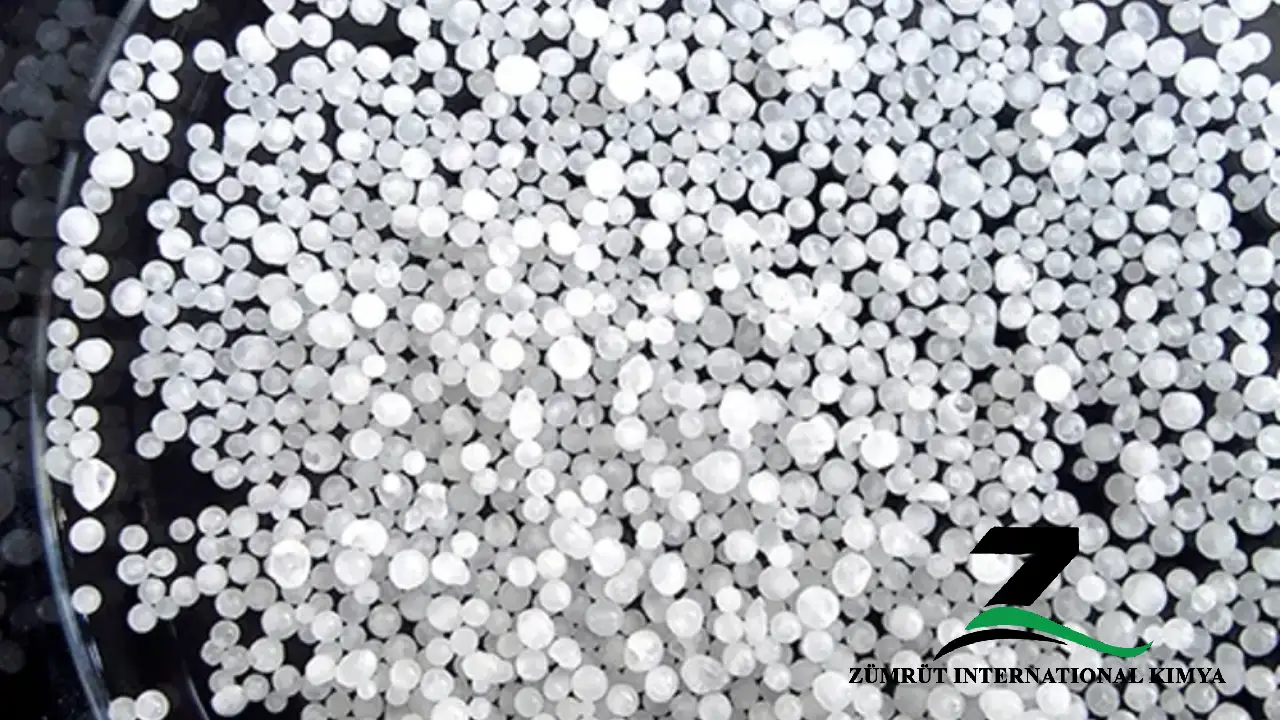
Caustic Soda Pearls – also known as sodium hydroxide pearls – are a solid form of caustic soda (NaOH), appearing as small, white, spherical granules. This form is particularly favored for its high purity, ease of handling, and efficient storage.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Caustic soda pearls are essentially spherical granules of sodium hydroxide. Their size often ranges between 0.5 mm and 2.0 mm in diameter, making them easy to store, handle, and measure out in various processes. As a deliquescent substance, caustic soda absorbs moisture from the environment and tends to dissolve if exposed to air for too long. This characteristic necessitates careful packaging and handling to maintain product integrity and safety.
Below is a table summarizing the typical specifications of caustic soda pearls provided by many reputable suppliers, including Zumrut kimya. These values may vary slightly depending on the manufacturer’s production processes and raw material sources, but they represent standard industry benchmarks:
| Parameter | Specification |
| Size | 0.50 mm – 2.00 mm dia. |
| Appearance | White deliquescent spheres |
| NaOH | 99% minimum |
| NaCl | 0.046% wt. (maximum) |
| Na₂CO₃ | 0.94% wt. (maximum) |
| Na₂SO₄ | 0.038% wt. (maximum) |
| Fe | 5 wt. ppm (maximum) |
| Ni pick-up | 3 wt. ppm (maximum) |
Key Properties
- Chemical Formula: NaOH
- Appearance: White, round pellets or pearls
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water, exothermic reaction
- Purity: Typically ≥ 99%
- CAS Number: 1310-73-2
Applications of caustic soda pearls
- Chemical Manufacturing
Used as a key raw material in the production of:
Soaps and detergents
Sodium-based chemicals (e.g., sodium hypochlorite, sodium phenolate)
Synthetic dyes and pigments - Pulp and Paper Industry
Employed in:
Kraft pulping process (digesting wood into pulp)
Bleaching of paper and pulp
Removal of lignin from wood fibers - Textile Industry
Used in:
Mercerizing cotton (enhancing strength and luster)
Scouring and bleaching fabrics
Dye fixation and pH control during processing - Water and Wastewater Treatment
For:
pH regulation of water
Neutralization of acidic effluents
Removal of heavy metals and organic contaminants - Oil and Gas / Petroleum Industry
Used in:
Drilling muds to increase alkalinity
Neutralizing acids in petroleum refining
Removing sulfurous impurities - Food Industry (with food-grade caustic soda)
Applications include:
Cleaning and sterilizing equipment
Peeling fruits and vegetables (e.g., tomatoes, potatoes)
Processing cocoa and chocolate - Soap and Detergent Production
Reacts with fats and oils in saponification to produce solid and liquid soaps
Used in industrial and household detergents - Metal Processing and Surface Treatment
Used for:
Aluminum etching
Descaling and degreasing of metals
Electroplating and galvanizing - Pharmaceuticals
As a pH adjuster and intermediate in the synthesis of various drugs - Biodiesel Production
Acts as a catalyst in the transesterification of vegetable oils and fats into biodiesel

Manufacturing Process Overview
- Brine Preparation
The production of caustic soda pearls begins with the preparation of a purified brine solution. Salt (commonly sodium chloride) is dissolved in water to create a concentrated brine. The quality of this salt—and the efficiency of brine purification—has a direct impact on the final caustic soda pearl quality. Excess ions, metals, and suspended solids must be removed through filtration, chemical precipitation, and other purification steps. - Electrolysis
Next comes the electrolysis stage, which is fundamental to the creation of sodium hydroxide. In the chlor-alkali process, the purified brine passes through an electrolytic cell. A direct current splits the sodium chloride solution into chlorine gas at the anode and a solution of sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas at the cathode. The resulting caustic solution must then be concentrated. - Concentration
After electrolysis, the sodium hydroxide solution typically contains around 30–35% NaOH. Through evaporation or other separation techniques, this solution is further concentrated to about 50%. This concentrated solution is crucial for the next stage—pearl formation. - Pearl Formation
In the final step, the concentrated caustic solution is passed through a prilling or pelletizing tower, where droplets of the molten sodium hydroxide solidify into small, spherical beads. These pearls are then cooled, screened to achieve the desired size (generally 0.5 to 2 mm), and packaged for distribution.
Package
25kg PP bag, 1000kg bag, 1200kg bag, etc
| LoadingDetails(20’FCL) | ||
| Packaging | WithPallet | WithoutPallet |
| 25kgppbag | 25mt | 28mt |
| 1000kgbigbag | 20mt | 20mt |
| 1200kgbigbag | 24mt | 24mt |
Technical Data Sheet of Caustic Soda Preals
| Property | Value | Unit |
| MeltingPoint: | 320-325 | ºC |
| BoilingPoint: | 1385-1390 | ºC |
| Densityat20ºC: | 2.13 | g/cm3 |
| SolutionRate:(100gin100mlwater at25ºC): |
22 | s |
| HeatCapacityat25ºC: | 2.01 | J/g.K |
| HeatofFusionat15ºC: | 167.5 | J/g |
| StandardHeat ofFormationat25 ºC: |
10.67 | kJ/g |
| Specifications | ||
| Item | Value | Unit |
| Purity: | 99.0 Min | % |
| Sodium Carbonate (Na2CO3): | 0.8 Max | % |
| Sodium Chloride (NaCl): | 0.05 Max | % |
| Fe2 O3: | 50 Max | PPM |
Technical Data Sheet of Caustic Soda Preals