Bitumen Emulsion for Slurry Seal
The asphalt surface of the roads can experience erosion, raveling, loss of aggregate, honeycombing, and sulphate attacks over time due to weather conditions such as frost, sunlight, heat, and also road salting, snow removal, as well as the effects of excessive loading and friction, especially caused by tire chains and snowplow blades. Failing to repair and install overlay asphalt in due time will allow damages to expand, leading to complete destruction of the road surface and even the underlying layers. The use of protective layers is recommended to prevent intensification of asphalt wear out, postpone overlay installation, maintain the existing conditions, and fill the cracks.
In addition to providing a suitable road surface, these layers will waterproof it and prevent the destruction of asphalt and its underlying layers. This is a cheap maintenance method that will ensure uninterrupted and secure operation of the roads. Different methods are recommended based on the degree of destruction, the weight and volume of traffic, and type of asphalt. These methods are inexpensive and can be employed early after or even before the beginning of asphalt pavement distress.
Slurry Seal is a cold mixture of fine graded aggregate, asphalt emulsion, mineral fillers, polymer and water applied to a pavement as a surface treatment. Slurry seal is used as both a preventive and corrective maintenance of asphalt pavement but is not intended to increase the structural strength of a pavement section. Our quality control staff works together with our customers to develop mix designs that enable us to provide you with the proper slurry seal oil for every application. The addition of polymers to our standard Slurry Seal oil increases durability and versatility.
Bitumen emulsion is a key material used in slurry seal, a thin surfacing technique for road maintenance and preservation. Slurry seal involves a mixture of aggregate, water, and bitumen emulsion, which is spread over a road surface to improve its texture, waterproofing, and durability.
A mixture of aggregates, water, CSS bitumen emulsion and filler (usually cement) that must be paved with special Slurry Seal paving machine. Slurry Seal not only fills the voids, but it helps the surface to be more resistant.
What is Bitumen Emulsion?
Bitumen emulsion is a fine dispersion of bitumen in water, stabilized by emulsifiers. It is used in road construction and maintenance because it is easy to handle, requires no heating, and adheres well to various surfaces. The bitumen emulsion can be classified as:
For slurry seal, cationic emulsions are more commonly used due to their better adhesion to aggregate and road surfaces.
Benefits of Using Bitumen Emulsion in Slurry Seal
- Ease of Application: Requires no heating, reducing energy consumption and environmental impact.
- Quick Setting: Suitable for roads that require quick reopening to traffic.
- Improved Surface Texture: Restores skid resistance and ride quality.
- Waterproofing: Protects the road base from water infiltration.
- Cost-Effective Maintenance: Extends the lifespan of roads without full reconstruction.
Typical Composition of a Slurry Seal Mix
- Bitumen Emulsion: Acts as a binder.
- Aggregate: Fine, graded aggregates for durability and smoothness.
- Water: Adjusts the consistency and helps with application.
- Additives: Enhance workability or adjust the setting time (e.g., retarders, accelerators).
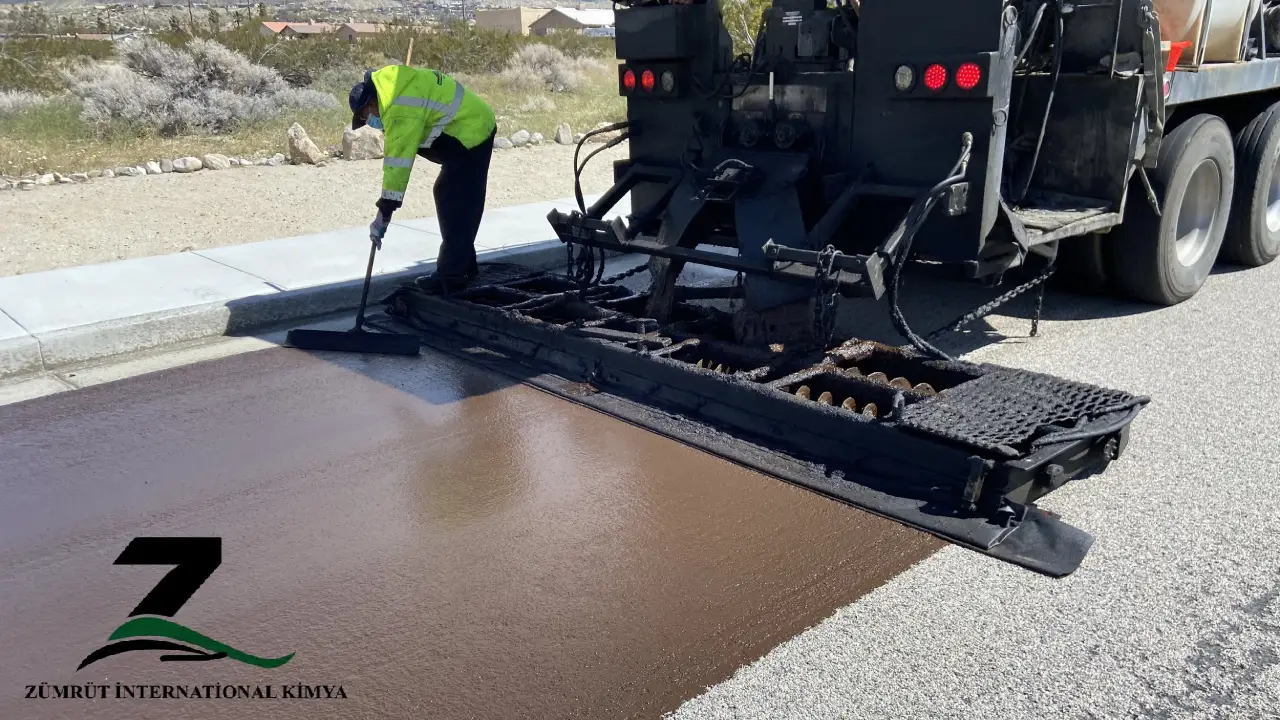

Application Process of Bitumen Emulsion for Slurry Seal
- Surface Preparation
– Cleaning: Remove dust, dirt, debris, oil, and loose particles from the existing road surface using brooms, blowers, or water jets.
– Patching: Fill cracks, potholes, and other surface defects to provide a uniform base.
– Tack Coat (if needed): Apply a thin layer of diluted bitumen emulsion to improve adhesion between the existing surface and the slurry seal. - Mixing
The slurry seal mixture is prepared on-site or nearby using a slurry seal mixing machine. The components are:
– Bitumen Emulsion: Acts as the binder.
– Aggregates: Well-graded and fine aggregates provide strength and texture.
– Water: Adjusts the mix consistency and aids in spreading.
– Additives: Retarders, accelerators, or stabilizers may be added to control the setting time and improve workability.
The mixing process ensures a homogeneous slurry with the proper proportions for the project. - Application
– The slurry seal mixture is loaded into a slurry spreader box, which is mounted on a specialized truck.
– The spreader box applies the slurry in a uniform layer across the road surface. The layer thickness typically ranges from 3 to 10 mm, depending on the intended use and traffic requirements.
– The spreader adjusts to maintain even coverage across the width of the road. - Finishing
– Leveling: The slurry is leveled as it is applied, ensuring a smooth surface finish.
– Joint Treatment: Care is taken at joints and overlaps to prevent unevenness and ensure a seamless connection with adjacent lanes or sections. - Curing
– The emulsion breaks (separates water from bitumen) and sets, bonding the aggregates to the road surface.
– Curing times vary depending on the emulsion type, temperature, and humidity, but roads are usually ready for light traffic within 2–6 hours. - Opening to Traffic
Once the slurry seal has fully cured and reached sufficient strength, the road is reopened to traffic. Proper curing ensures:
– No tracking or displacement of the slurry seal.
– Durable adhesion of the seal to the road.
What type of asphalt emulsion is suitable?
Cationic slow-setting emulsions are used. They are selected on the basis of a laboratory mix design process, which involves tests on the compatibility of the aggregate and the emulsion, and on the durability of the cured seals.

Best Practices
- Weather Conditions: Avoid application during rain, high humidity, or extreme temperatures.
- Traffic Control: Implement proper traffic management to keep the area clear during application and curing.
- Quality Assurance: Monitor the mix proportions, application rate, and layer uniformity to meet project specifications.
What is slurry surfacing?
Slurry surfacing is a thin dense-graded cold mixed overlay. Slurry seal are thin layers rich in asphalt used for residential streets, airports and in some countries for sidewalks and parking lots. Microsurfacing is a premium product based on specially selected aggregates and polymer modified asphalt emulsion. Microsurfacing is designed to be applied in thicker lifts for high trafficked areas.
How is a slurry seal or microsurfacing applied?
Normally, aggregate, emulsion, water, and filler such as cement are mixed in a mobile mix paver and the mixture which has a slurry-like consistency is allowed to fall into a ‘spreader box’ which distributes it over the road surface to a predetermined thickness. Slurry surfacings may also be hand applied. The slurry cures rapidly (typically within 1 or 2 hours) and traffic can be allowed on it.
Slurry Seal applications and facts:
- Type 1: Used in low traffic area such as private and residential roadways
- Type 2: Most commonly used slurry. Used for moderate to high traffic roadways
- Type 3: Used for high volume roads and heavier traffic